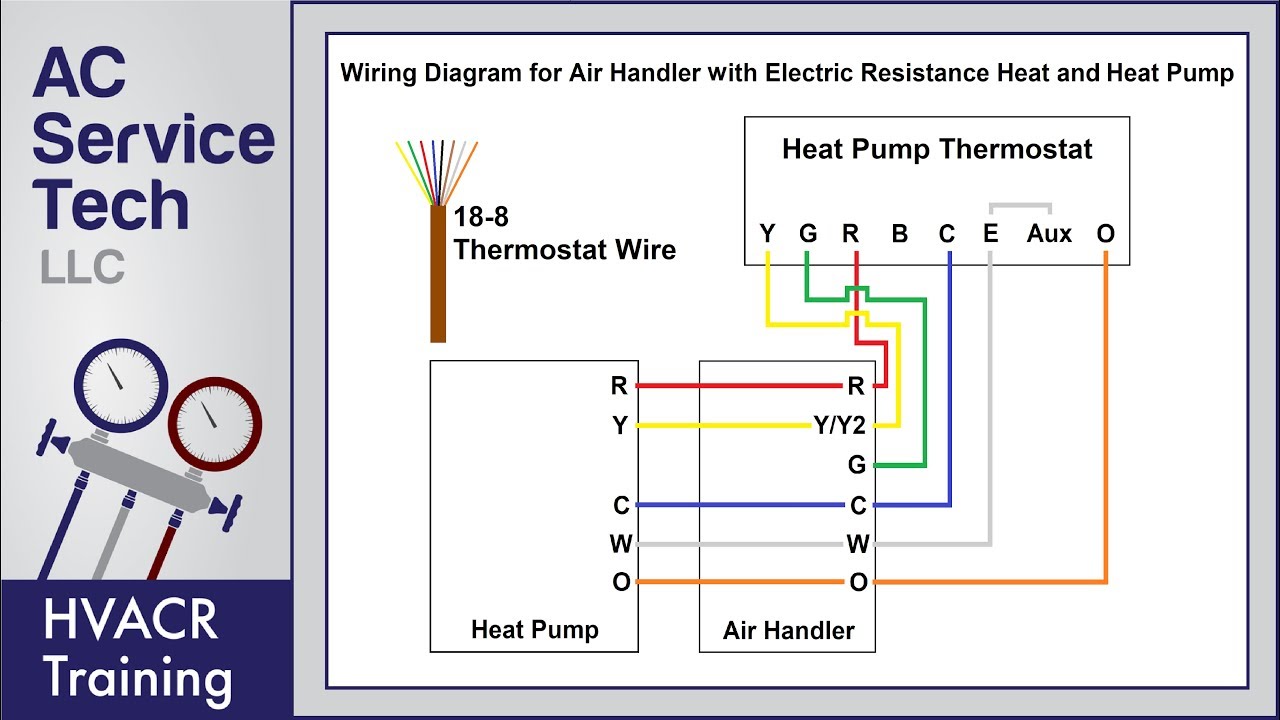
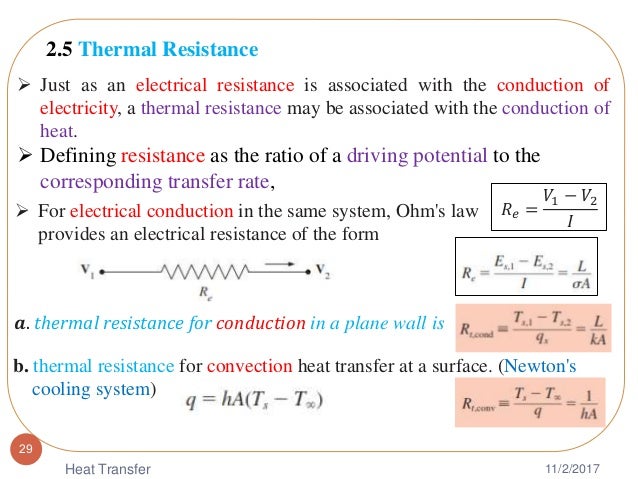
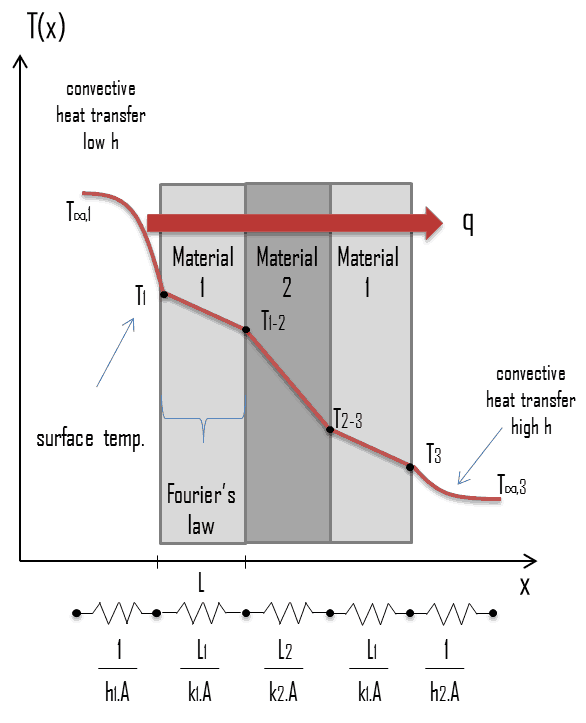
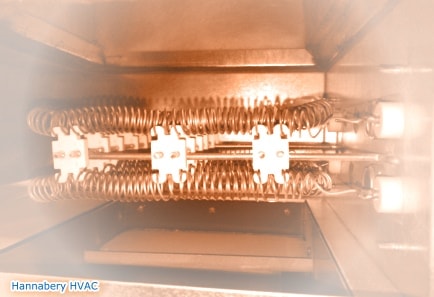
At lower outdoor temperatures the heat pump essentially runs continuously and supplemental heat typically from electric resistance heaters must be provided to satisfy the building heating load.
Electric resistance heating definition.
Electric heating is a process in which electrical energy is converted to heat energy common applications include space heating cooking water heating and industrial processes.
There are two methods of electric resistance heating.
Resistance heaters produce heat by passing an electric current through a resistance a coil wire or other obstacle which impedes current and causes it to give off heat.
The heating element inside every electric heater is an electrical resistor and works on the principle of joule heating.
When a voltage is applied across a substance there will be an.
If the resistance is high a large amount of heat is generated and the material is used as a resistor rather than as a conductor.
Electric resistance heat can be supplied by centralized forced air electric furnaces or by heaters in each room.
Direct electric resistance heating and.
The degree of heating for a given current is proportional to the electrical resistance of the conductor.
Whenever an electric current flows through a material that has some resistance i e anything but a superconductor it creates heat.
Resistance heating definition is heating by means of energy produced by the passing of electric current through resistance units.
A special design feature of recently developed heat pumps for northern climates is the 3 piece or triple split design in which the compressor is.
Heaters of this kind have an inherent efficiency of 100 in converting electric energy into heat.
This resistive heating is the result of friction as created by microscopic phenomena such as retarding forces and collisions involving the charge carriers usually electrons.
Electric resistance heating is defined as the heat produced by passing an electric current through a material that preferably has high resistance as the current passes through the material ohmic losses i 2 r losses occur these losses cause the conversion of electrical energy into heat.
Definition of electrical resistance resistance also known as ohmic resistance or electrical resistance is a measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit.
In formal terminology the heat corresponds to the work done by the charge.
Resistance is measured in ohms symbolized by the greek letter omega ω.
Joule heating also known as resistive resistance or ohmic heating is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor produces heat.
Joule s first law also known as the joule lenz law states that the power of heating generated by an electrical conductor is proportional to the product of its resistance and the square of the current.